What Type of Member Functions Allow a Client of a Class to Assign Values to Private Data Members?
Class: A form in C++ is the building block that leads to Object-Oriented programming. It is a user-divers data type, which holds its own data members and member functions, which tin be accessed and used by creating an instance of that class. A C++ class is like a design for an object.
For Example: Consider the Class of Cars. There may be many cars with different names and make but all of them will share some common backdrop like all of them will accept four wheels, Speed Limit, Mileage range etc. So here, Car is the class and wheels, speed limits, mileage are their properties.
- A Class is a user defined information-type which has data members and member functions.
- Data members are the data variables and fellow member functions are the functions used to manipulate these variables and together these data members and member functions defines the backdrop and behavior of the objects in a Class.
- In the above instance of class Car, the data member volition be speed limit, mileage etc and member functions tin be apply brakes, increase speed etc.
An Object is an instance of a Grade. When a class is divers, no retentiveness is allocated just when it is instantiated (i.east. an object is created) memory is allocated.
Defining Course and Declaring Objects
A course is divers in C++ using keyword class followed by the name of class. The body of class is defined within the curly brackets and terminated by a semicolon at the terminate.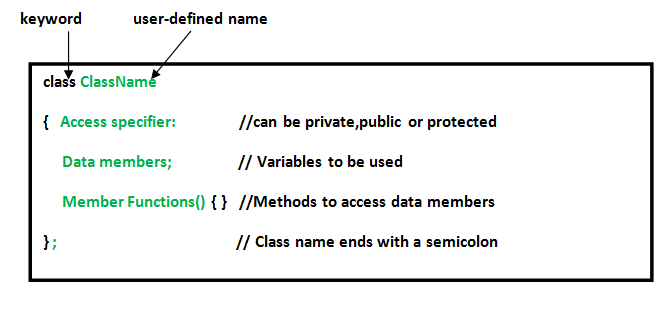
Declaring Objects: When a class is defined, merely the specification for the object is defined; no memory or storage is allocated. To use the data and access functions defined in the class, you need to create objects.
Syntax:
ClassName ObjectName;
Accessing information members and fellow member functions: The data members and member functions of class can be accessed using the dot('.') operator with the object. For example if the proper noun of object is obj and you want to access the member function with the name printName() and so you will have to write obj.printName() .
Accessing Data Members
The public data members are also accessed in the same way given however the private data members are not allowed to be accessed directly by the object. Accessing a information fellow member depends solely on the access control of that data member.
This access control is given by Access modifiers in C++. There are three access modifiers : public, individual and protected.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Geeks
{
public :
string geekname;
void printname()
{
cout << "Geekname is: " << geekname;
}
};
int main() {
Geeks obj1;
obj1.geekname = "Abhi" ;
obj1.printname();
render 0;
}
Output:
Geekname is: Abhi
Member Functions in Classes
At that place are 2 means to define a member function:
- Within form definition
- Outside class definition
To define a member office outside the form definition nosotros have to use the scope resolution :: operator along with class name and function name.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Geeks
{
public :
cord geekname;
int id;
void printname();
void printid()
{
cout << "Geek id is: " << id;
}
};
void Geeks::printname()
{
cout << "Geekname is: " << geekname;
}
int main() {
Geeks obj1;
obj1.geekname = "xyz" ;
obj1.id=xv;
obj1.printname();
cout << endl;
obj1.printid();
return 0;
}
Output:
Geekname is: xyz Geek id is: 15
Annotation that all the member functions defined inside the class definition are by default inline, only you can besides make whatsoever non-course office inline past using keyword inline with them. Inline functions are actual functions, which are copied everywhere during compilation, like pre-processor macro, then the overhead of part calling is reduced.
Annotation: Declaring a friend function is a way to requite private access to a non-fellow member function.
Constructors
Constructors are special class members which are called by the compiler every time an object of that class is instantiated. Constructors take the same name as the class and may be divers inside or outside the course definition.
There are 3 types of constructors:
- Default constructors
- Parameterized constructors
- Copy constructors
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Geeks
{
public :
int id;
Geeks()
{
cout << "Default Constructor chosen" << endl;
id=-ane;
}
Geeks( int x)
{
cout << "Parameterized Constructor called" << endl;
id=x;
}
};
int main() {
Geeks obj1;
cout << "Geek id is: " <<obj1.id << endl;
Geeks obj2(21);
cout << "Geek id is: " <<obj2.id << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Default Constructor chosen Geek id is: -1 Parameterized Constructor called Geek id is: 21
A Re-create Constructor creates a new object, which is verbal re-create of the existing object. The compiler provides a default Copy Constructor to all the classes.
Syntax:
class-name (course-name &){} Destructors
Destructor is another special member function that is chosen by the compiler when the scope of the object ends.
#include <$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Geeks
{
public :
int id;
~Geeks()
{
cout << "Destructor called for id: " << id <<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Geeks obj1;
obj1.id=7;
int i = 0;
while ( i < 5 )
{
Geeks obj2;
obj2.id=i;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Destructor called for id: 0 Destructor chosen for id: 1 Destructor chosen for id: 2 Destructor called for id: three Destructor chosen for id: 4 Destructor called for id: 7
Pure Virtual Destructor
Related Articles:
- Multiple Inheritance in C++
- C++ Quiz
This article is contributed by Abhirav Kariya. If you lot similar GeeksforGeeks and would similar to contribute, you can also write an commodity using write.geeksforgeeks.org or postal service your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Encounter your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks principal page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if y'all observe anything incorrect, or y'all want to share more information about the topic discussed in a higher place.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-classes-and-objects/
Belum ada Komentar untuk "What Type of Member Functions Allow a Client of a Class to Assign Values to Private Data Members?"
Posting Komentar